Immune cell markers are molecules expressed on the surface and within immune cells that enable researchers to identify and characterize different immune cell phenotypes. Immune cell phenotyping can be performed using multiplex flow cytometry or multiplex immunohistochemistry. Antibodies targeting immune cell markers are essential tools for immunology research as they enable observation of which immune cells are present in a given sample. Scientists can also combine antibodies for immune cell markers with markers of function and cell state, as well as with antibodies for therapeutic targets. These experiments can shed light on the immune system's role in disease progression and therapeutic response.
To gain a deeper understanding of which cell types are present in a tissue sample and their potential role in disease progression or therapeutic response, scientists observe specific immune cell markers such as CD8 to identify cytotoxic T cells, CD68 to identify macrophages, and FoxP3 to identify regulatory T cells. Immune cell markers such as these are essential for identifying immune cell types and their contributions to immune responses. Additionally, researchers often examine markers that are indicative of immune cell function, including mediators that may be secreted by cells (e.g., IL-8, Granzyme B), pathway activation indicators (e.g., phosphorylation of STATs), and receptors that activate or inhibit immune cell function (e.g., ICOS, PD-1).
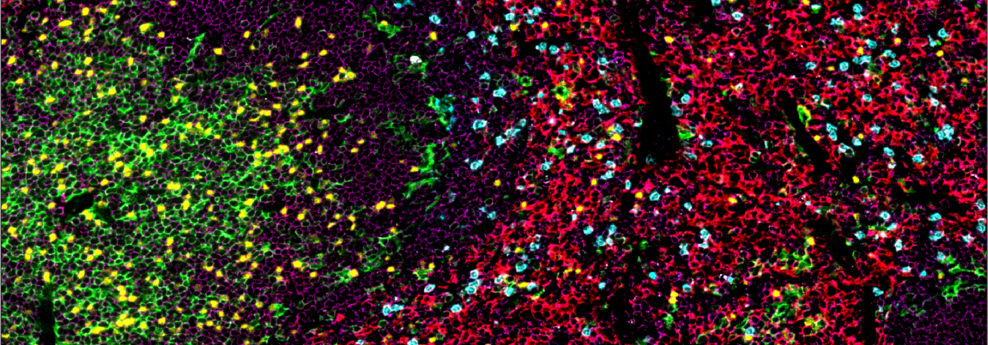
When studying immune responses, scientists increasingly apply spatial biology techniques, such as multiplex immunohistochemistry (mIHC), that enable observation of immune responses in FFPE tissue samples. This approach allows researchers to examine the spatial organization of immune cells and gain insights into the location of immune cell subsets within a tissue, the proximity of different cell types to one another, and immune structures such as tertiary lymphoid structures.
Antibodies for immune phenotyping and functional markers are indispensable for maximizing the potential of IHC and mIHC techniques in immunology research. Intricate mIHC visuals offer more than pretty images—they provide robust datasets that add spatial context to quantifiable expression and activation information. Studies leveraging antibodies for immune phenotyping and functional markers in mIHC experiments often lead to critical insights into the immune system's role in disease and therapy. Therefore, antibodies targeting immune cell markers are not only tools for discovery, but also pivotal assets for advancing translational and clinical research.
CST offers a comprehensive portfolio of rigorously validated, top-performing recombinant antibodies that target immune cell markers and functional markers for analysis in FFPE tissue. These antibodies empower scientists to confidently analyze and extract meaningful data from every precious tissue sample. CST® antibodies are compatible with low-, mid-, and high-plex multiplex IHC platforms and are available in multiple formats, including:
Discover the breadth of high-quality, IHC-validated antibodies CST has to offer for immunology markers and immunotherapy research targets.
Some of the following approaches are used at CST to validate our antibodies for IHC.